The House dug right in upon its early return to Capitol Hill this week. The Democratic leadership succeeded in resolving differences within its caucus to pass the $3.5 trillion budget blueprint approved by the Senate before the August recess. The blueprint allows work to begin on legislation that sets funding for President Joe Biden’s social priorities in his Build Back Better plan, including investments in public health, education, environment, and climate change. As in the Senate, there was no Republican support for the budget resolution in the House.
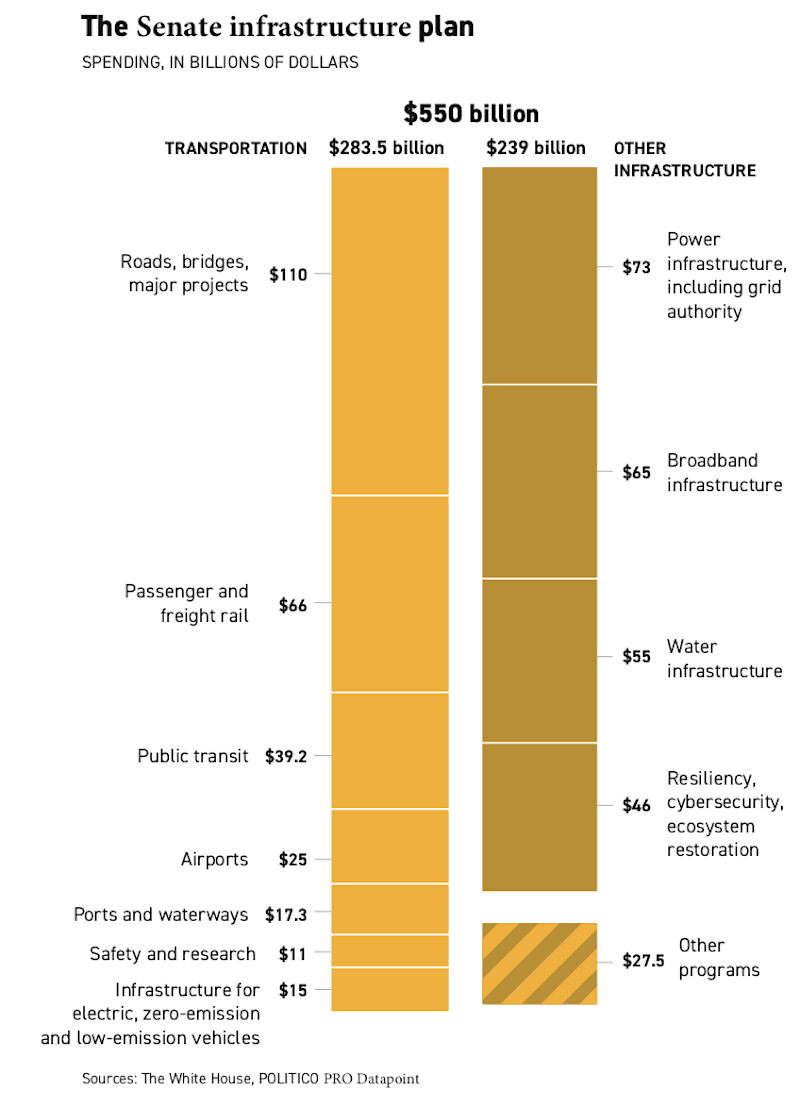
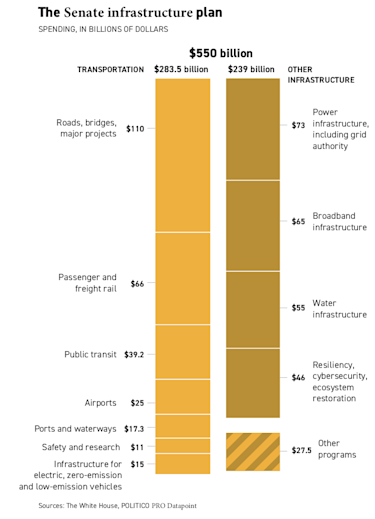
The vote paves the way for passage of the bipartisan infrastructure bill by Sept. 27. The measure also passed the Senate before the recess. Nineteen Republicans joined all 50 Democrats on this significant investment in the nation’s public works. The package represents $550 billion in new federal funding, including $110 billion for roads and bridges, $73 billion to rebuild the electric grid, $66 billion in passenger and freight rail, $65 billion to expand broadband internet access, $55 billion for water infrastructure, $39 billion to modernize public transit like buses, and $7.5 billion to create the first federal network of charging stations for electric vehicles. AMT joined other manufacturing organizations calling on the Senate to pass the measure.
Now, House Democrats must work in earnest to write the sweeping legislation that details how much to spend and how to pay for it. Moderate Senators warn the current price tag and the pay-fors attached to it could change their votes to no. The razor thin Democratic majorities in both chambers require House Speaker Nancy Pelosi, D-Calif., to unite her members behind a comprehensive spending bill that doesn’t lose any support in the Senate.
These are fast-changing developments. We’ll continue to provide updates as action warrants.